Introduction
As the electric vehicle (EV) market continues to expand, manufacturers are constantly exploring advanced materials to improve performance, range, and durability. Titanium components are gaining attention in the design and construction of electric cars for their exceptional properties.
 [1]
[1]
This article discusses the role of titanium in EVs. Hope that you can learn about its benefits and the transformative impact.
Why Titanium for Electric Cars?
Titanium is notable for its exceptional strength, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. Ti components offer a range of benefits that make it a preferred material for various EV applications.
- Weight Reduction: One of the primary challenges in electric car design is managing weight, particularly because of the heavy batteries needed for adequate range. Titanium comes with high strength-to-weight ratio. So, it is ideal for reducing the overall weight of vehicles. That directly enhances battery efficiency and increases range.
- Durability: Titanium’s corrosion resistance extends the life of car components exposed to harsh conditions. This is particularly beneficial for undercarriage parts and battery casings because they are susceptible to road salt and other corrosive elements.
- High-Temperature Performance: Electric vehicles require materials that can withstand high temperatures, especially in the battery and motor assemblies. Titanium component excel in high-temperature environments. They are able to maintain its strength and resisting deformation.
How Titanium Is Used in Electric Cars?
With superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, Ti has become a key material in the automotive industry.
- Battery Packs: Ti finds use in the frames and casings of battery packs to protect them from physical damage and thermal issues. Its lightweight nature helps mitigate the weight of the batteries, allowing for larger packs that do not excessively increase the overall weight of the vehicle.
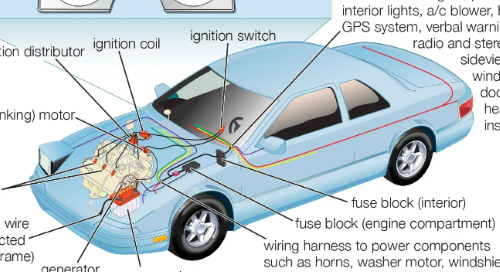
- Structural Components: Using titanium in the structural framework of electric vehicles, such as in the chassis and body panels, brings several significant benefits. Primarily, the metal’s lightness significantly reduces the overall vehicle weight. This reduction is crucial and makes the EVs quicker and more responsive.
- Motor Components: Ti’s excellent heat resistance makes it suitable for use in electric motors, where components must operate reliably at high temperatures generated during operation.
| Component | Application of Titanium | Benefits |
| Battery Packs | Frames and casings | Protects from physical damage and thermal issues; allows for larger battery packs without significantly increasing vehicle weight. |
| Structural Components | Chassis, body panels | Reduces vehicle weight; enhances efficiency and handling; contributes to better acceleration and responsiveness. |
| Motor Components | Components in electric motors | Maintains integrity and performance at high operating temperatures; ensures reliability and durability of motor parts. |
Related reading: Applications Of Titanium Alloy In The Automobile Industry
Challenges in Adopting Titanium
- Cost: The primary barrier to widespread use of titanium in electric vehicles is its cost. Titanium component processing is expensive, and the material itself is more costly than traditional automotive materials like steel or aluminum.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Working with titanium can be challenging due to its hardness and special handling requirements during manufacturing. This includes difficulties in welding and machining, which require specialized equipment and skills.
Future Prospects
As technology progresses and the demand for more efficient and high-performance electric vehicles grows, the potential for titanium use in the industry is significant. Advances in material science and manufacturing technology may reduce the cost and complexity of working with titanium. Furthermore, as more automotive manufacturers commit to sustainable and efficient vehicle production, the high recycling rate and durability of titanium could make it an even more attractive option.
Conclusion
Titanium in electric cars holds a promising future. Its exceptional properties offer substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, performance, and vehicle longevity. While there are challenges associated with its cost and manufacturing, ongoing advancements are likely to expand its role in the EV industry. As manufacturers continue to innovate and prioritize advanced materials, titanium’s presence in electric cars is poised to grow, marking a significant step forward in automotive technology.
Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) is a leading supplier of titanium products. ARM customizes materials according to specific customer specifications and drawings, ensuring flexibility and precision for diverse project needs. Send us an inquiry if you are interested.
Reference:
[1] Chassis. (2024, April 23). In Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/technology/automobile/Cooling-system