Tantalum is a rare, corrosion-resistant metal used in industries like electronics, medical devices, and aerospace. Tantalum powder, in its various forms, plays a critical role in manufacturing applications requiring precision and reliability.
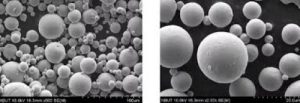
Types of Tantalum Powder
1. Capacitor-Grade Tantalum Powder
Capacitor-grade tantalum powder is highly pure and finely structured, with precisely controlled particle size. It is specifically designed for producing electrolytic capacitors. These capacitors are crucial in devices such as smartphones, automotive systems, and medical electronics due to their high capacitance and compact size.
2. Spherical Tantalum Powder
Spherical tantalum powder is produced using techniques like gas atomization, resulting in uniform, smooth particles with excellent flowability. Spherical tantalum powder is ideal for 3D printing and metal injection molding (MIM). Industries such as aerospace, biomedical, and defense use it to manufacture high-precision components, including prosthetics and jet engine parts.
Further reading: Spherical Tantalum Powder: Advantages and Applications
3. Nodular Tantalum Powder
Nodular tantalum powder is characterized by its irregular particles and large surface area, which enhances performance in specific applications. It is primarily used in the production of high-voltage tantalum capacitors. The increased surface area improves charge storage efficiency, making it ideal for advanced capacitor technology.
4. High-Purity Tantalum Powder
High-purity tantalum powder, with purity levels exceeding 99.99%, is used in applications where impurities can compromise performance. It is essential for semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature aerospace applications, such as superalloys that require exceptional strength and heat resistance.
5. Coarse Tantalum Powder
Coarse tantalum powder consists of larger, irregular particles with a lower surface area. It is commonly used in metallurgical applications, including sintered components and tantalum mill products such as rods, sheets, and wires.
Production Methods
The production method determines the powder’s particle size and morphology. Chemical reduction of tantalum pentoxide (Ta₂O₅) with magnesium or sodium produces fine powders. Gas atomization creates spherical powders by melting tantalum and spraying it with inert gas. For coarse powders, hydrogen decrepitation is used to break down tantalum ingots.
Applications of Tantalum Powder
Tantalum powders are indispensable in various industries.
In electronics, capacitor-grade Ta powders are used for tantalum capacitors, which power electronic circuits in consumer devices, medical implants, and automotive electronics. The high-purity variants are also essential for semiconductors requiring minimal contamination.
In aerospace, Ta powders, particularly spherical types, are used to produce components like turbine blades, heat shields, and other parts that withstand high temperatures and corrosive conditions.
In medical applications, Ta’s biocompatibility makes it suitable for bone implants, dental prosthetics, and other medical devices that require strength, durability, and safety.
The growing adoption of 3D printing technologies has increased the demand for spherical Ta powder, which enables the creation of complex, lightweight, and highly durable parts.
Common Types of Tantalum Powder
| Type | Description | Applications |
| Capacitor-Grade | High purity, fine particle size. | Electrolytic capacitors (electronics). |
| Spherical | Uniform, smooth particles, flowable. | 3D printing, aerospace, biomedical. |
| Nodular | Irregular shape, large surface area. | High-voltage capacitors. |
| High-Purity | 99.99%+ purity, impurity-free. | Semiconductors, aerospace superalloys. |
| Coarse | Large, irregular particles. | Metallurgy, sintered components. |
This table provides a concise overview of each powder type, highlighting their unique characteristics and main areas of application. For more information, please check Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM).
Conclusion
Tantalum powder, available in capacitor-grade, spherical, nodular, high-purity, and coarse forms, serves as a critical material across multiple industries. Its unique properties, including corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and high temperature tolerance, make it indispensable in electronics, aerospace, and medical manufacturing. Advances in production methods, like gas atomization and chemical reduction, continue to enhance the quality and versatility of tantalum powders, enabling innovations in modern technology and engineering.
















Recent Comments