Introduction:
In the world of materials science and technological advancements, certain elements play a crucial role in driving innovation and progress. Tantalum chloride, with its unique properties and versatile applications, stands out as one such catalyst for transformative developments. From electronics to chemical synthesis, tantalum chloride has made its mark across various industries, propelling us toward a future of endless possibilities.
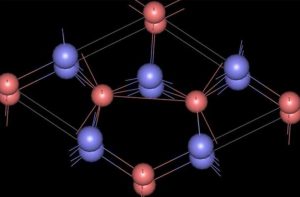
Understanding Tantalum Chloride:
Tantalum chloride, chemically represented as TaCl5, is a compound composed of tantalum and chlorine atoms. It exists as a white or pale yellow solid at room temperature and is highly soluble in organic solvents. With its distinctive characteristics, tantalum chloride serves as a vital building block for numerous scientific and technological endeavors.
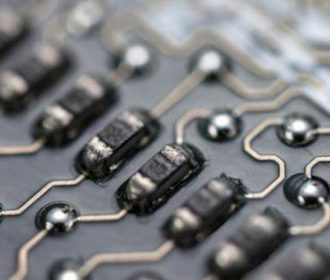
Electronic Applications:
The electronics industry heavily relies on tantalum chloride due to its exceptional conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It is a key component in the production of tantalum capacitors, which find extensive usage in smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices. Tantalum chloride’s ability to store and release electrical energy efficiently has contributed to the miniaturization and improved performance of electronic gadgets.
Chemical Synthesis and Catalysis:
Tantalum chloride plays a pivotal role in the field of chemical synthesis and catalysis. It acts as a catalyst, facilitating various reactions and accelerating chemical transformations. Tantalum chloride catalysts find application in organic synthesis, polymerization processes, and the production of specialty chemicals. Their ability to enhance reaction rates, selectivity, and yield has revolutionized the field of chemical manufacturing.
Nanotechnology and Materials Science:
The fascinating properties of tantalum chloride have also made it an essential component in the realm of nanotechnology and materials science. It is used in the fabrication of thin films, coatings, and nanoparticles with tailored properties. Tantalum chloride’s ability to control crystal growth, modify surface characteristics, and improve material performance has opened new avenues in the development of advanced materials for various industries.
Energy and Sustainability:
Tantalum chloride’s contributions extend to the energy sector as well. It is utilized in the production of solid oxide fuel cells, which have the potential to revolutionize clean energy generation. Tantalum chloride-based materials enable efficient conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, offering a sustainable solution for power generation while reducing environmental impact.
Future Prospects and Challenges:
As tantalum chloride continues to drive innovation and progress, there are certain challenges that need to be addressed. The responsible sourcing and sustainable extraction of tantalum are critical to ensuring its long-term availability. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on exploring new applications and improving the efficiency of tantalum chloride-based technologies.
Conclusion:
Tantalum chloride stands as a remarkable catalyst for innovation and progress in various industries. It’s unique properties and versatile applications have propelled advancements in electronics, chemical synthesis, nanotechnology, energy, and beyond. As we delve further into the realm of tantalum chloride, we unlock the doors to a future where technology, sustainability, and human ingenuity converge to shape a better world.
For more info, please visit: https://www.samaterials.com/


















Recent Comments